A regular expression is also spelled as regexp which holds a regular expression, used to match a pattern against strings. In Ruby, a pattern is written between forward slash characters. They describe the content of a string. Ruby regular expression is more similar to Perl regular expression.
Syntax:
/search string/ Ruby 1.9 uses Oniguruma regular expressions library but Ruby 2.0 uses Onigmo regular expressions library. Onigmo is a fork library of Oniguruma adding some new features.
=∽ and #match operators
The pattern matching is achieved by using =∽ and #match operators.Backward Skip 10sPlay VideoForward Skip 10s
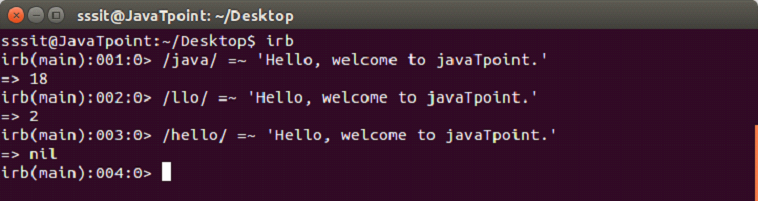
=∽
This is the basic matching pattern. Here two operands are used. One is a regular expression and other is a string. The regular expression is matched with the string.
If a match is found, the operator returns index of first match otherwise nil.
Example:
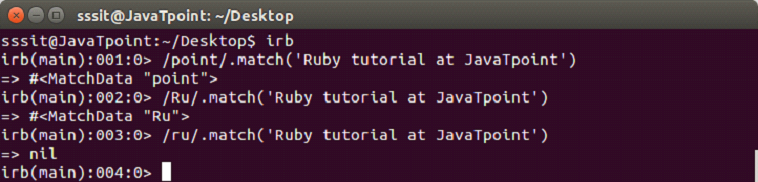
#match
This operator returns a MatchData object on matching otherwise nil.
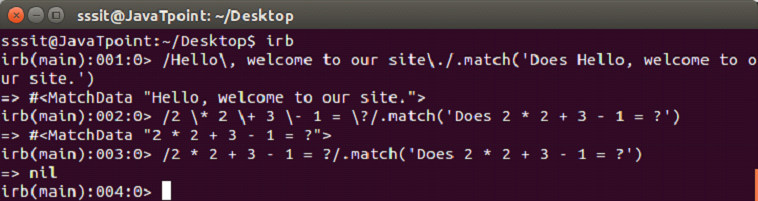
Metacharacters and Escapes
Metacharacters have specific meaning in a pattern. To match a string, they are back slashed (\\\) or escaped. Some meta characters are (,), (.), (?), (+), (-), (*), [,], {,}.
It returns the specific string when matched otherwise nil.
Example:
Characters Classes
Metacharacters have specific meaning in a pattern. To match a string, they are back slashed (\\\) or escaped.
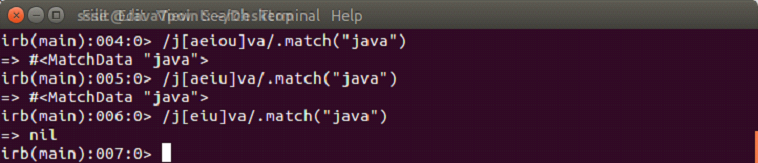
A character class is encircled within square brackets.
[ab]
Here, [ab] means a or b. It is the oppoite of /ab/ which means a and b.
Example:
[a-d]
Here, [a-d] is equivalent to [abcd]. The hyphen (-) character class represents range of characters.
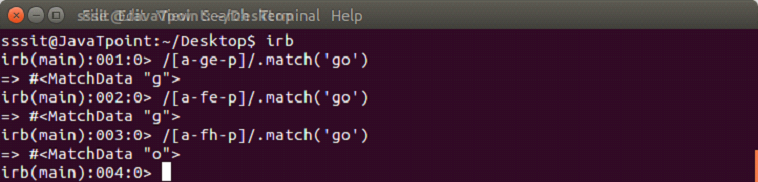
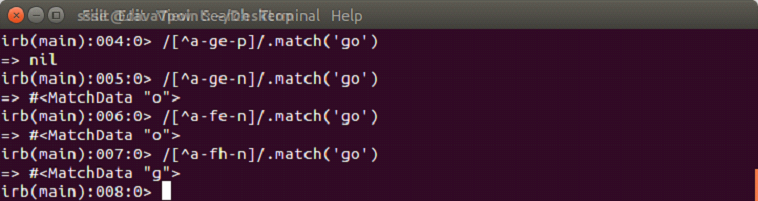
[^a-d]
The ^ sign represents any other character which is not present in the range.
Example:
Leave a Reply