Iterator is a concept used in object-oriented language. Iteration means doing one thing many times like a loop.
The loop method is the simplest iterator. They return all the elements from a collection, one after the other. Arrays and hashes come in the category of collection.
Ruby Each Iterator
The Ruby each iterator returns all the elements from a hash or array.
Syntax:
(collection).each do |variable|
code...
endHere collection can be any array, range or hash.
Example:
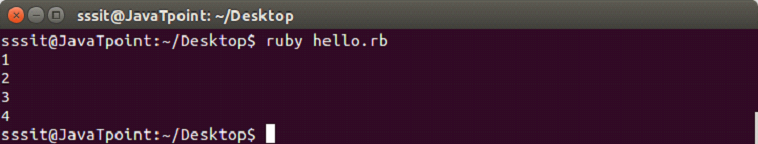
#!/usr/bin/ruby
(1...5).each do |i|
puts i
endOutput:
Ruby Times Iterator
A loop is executed specified number of times by the times iterator. Loop will start from zero till one less than specified number.
Syntax:
x.times do |variable|
code...
endHere, at place of x we need to define number to iterate the loop.
Example:
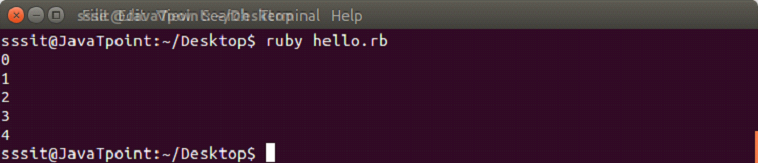
#!/usr/bin/ruby
5.times do |n|
puts n
endOutput:
Ruby Upto and Downto Iterators
An upto iterator iterates from number x to number y.
Syntax:
x.upto(y) do |variable|
code
endExample:
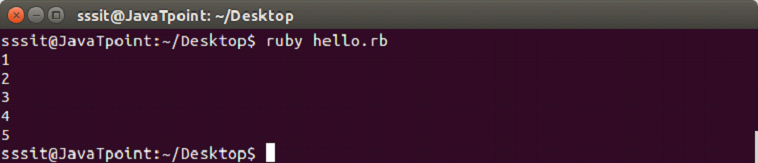
#!/usr/bin/ruby
1.upto(5) do |n|
puts n
endOutput:
Ruby Step Iterator
A step iterator is used to iterate while skipping over a range.
Syntax:
(controller).step(x) do |variable|
code
endHere, x is the range which will be skipped during iteration.
Example:
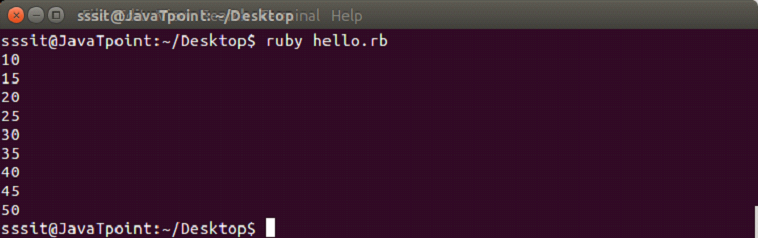
#!/usr/bin/ruby
(10..50).step(5) do |n|
puts n
endOutput:
Ruby Each_Line Iterator
A each_line iterator is used to iterate over a new line in a string.
Example:
#!/usr/bin/ruby
"All\nthe\nwords\nare\nprinted\nin\na\nnew\line.".each_line do |line|
puts line
end
Leave a Reply