What is Demand Forecasting?
Demand forecasting is a process of predicting the demand for an organisation’s products or services in a specified time period in the future. Demand forecasting is helpful for both new as well as existing organizations in the market

For Example, for various needs for demand forecasting in business organizations, a new organisation needs to anticipate demand to expand its scale of production. On the other hand, an existing organisation requires demand forecasts to avoid problems, such as overproduction and underproduction.
Demand forecasting enables an organisation to arrange for the required inputs as per the predicted demand, without any wastage of materials and time.
Table of Content [Show]
Organisations forecast demand in short term or long term depending on their requirements.
Short-term forecasting is done for coordinating routine activities, such as scheduling production activities, formulating pricing policy, and developing an appropriate sales strategy.
On the contrary, long-term forecasting is performed for planning a new project, expansion, and upgradation of production plant, etc.
There are a number of techniques for forecasting demand. Some of the popular techniques of demand forecasting are survey methods and statistical methods.
Also Read: What is Demand?
Concept of Demand Forecasting
In order to mitigate risks, it is of paramount importance for organisations to determine the future prospects of their products and services in the market. This knowledge of the future demand for a product or service in the market is gained through the process of demand forecasting.
Demand forecasting can be defined as a process of predicting the future demand for an organisation’s goods or services.
It is also referred to as sales forecasting as it involves anticipating the future sales figures of an organisation.
Also Read: What is Supply?
Demand Forecasting Definition
Some of the popular definitions of demand forecasting are as follows:
Demand estimation (forecasting) may be defined as a process of finding values for demand in future time periods.Evan J. Douglas
Demand forecasting is an estimate of sales during a specified future period based on proposed marketing plan and a set of particular uncontrollable and competitive forces.Cundiff and Still
Demand forecasting helps an organisation to take various business decisions, such as planning the production process, purchasing raw materials, managing funds, and deciding the price of its products.
Demand can be forecasted by organisations either internally by making estimates called guess estimate or externally through specialised consultants or market research agencies.
Also Read: Law of Demand
Components of Demand Forecasting
Let us discuss the basis components of demand forecasting in detail:
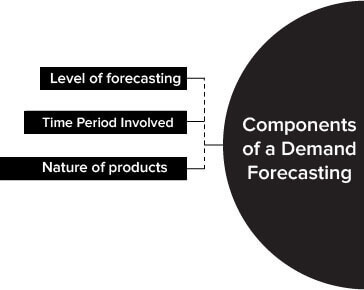
Level of forecasting
Demand forecasting can be done at the firm level, industry level, or economy level. At the firm level, the demand is forecasted for the products and services of an individual organisation in the future. At the industry level, the collective demand for the products and services of all organisations in a particular industry is forecasted. On the other hand, at the economy level, the aggregate demand for products and services in the economy as a whole is anticipated.
Time period involved
On the basis of the duration, demand is forecasted in the short run and long term, which is explained as follows:
- Short-term forecasting: It involves anticipating demand for a period not exceeding one year. It is focused on the shortterm decisions (for example, arranging finance, formulating production policy, making promotional strategies, etc.) of an organisation.
- Long-term forecasting: It involves predicting demand for a period of 5-7 years and may extend for a period of 10 to 20 years. It is focused on the long-term decisions (for example, deciding the production capacity, replacing machinery, etc.) of an organisation.
Nature of products
Products can be categorised into consumer goods or capital goods on the basis of their nature. Demand forecasting differs for these two types of products, which is discussed as follows:
- Consumer goods: The goods that are meant for final consumption by end users are called consumer goods. These goods have a direct demand. Generally, demand forecasting for these goods is done while introducing a new product or replacing the existing product with an improved one.
- Capital goods: These goods are required to produce consumer goods; for example, raw material. Thus, these goods have a derived demand. The demand forecasting of capital goods depends on the demand for consumer goods. For example, prediction of higher demand for consumer goods would result in the anticipation of higher demand for capital goods too.
Also Read: Law of Supply
Importance of Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is vital to the management of every business. It enables an organisation to mitigate business risks and make effective business decisions.
Moreover, demand forecasting provides insight into the organisation’s capital investment and expansion decisions.
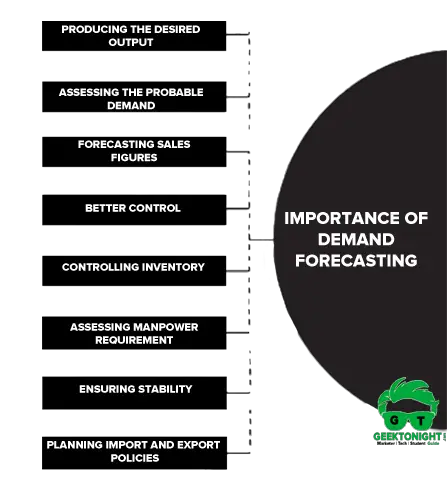
Importance of Demand forecasting are:
- Producing the desired output
- Assessing the probable demand
- Forecasting sales figures
- Better control
- Controlling inventory
- Assessing manpower requirement
- Ensuring stability
- Planning import and export policies
Producing the desired output
Demand forecasting enables an organisation to produce the pre-determined output. It also helps the organisation to arrange for the various factors of production (land, labour, capital, and enterprise) beforehand so that the desired quantity can be produced without any hindrance.
Assessing the probable demand
Demand forecasting enables an organisation to assess the possible demand for its products and services in a given period and plan production accordingly. In this way, demand forecasting avoids dependence on merely making assumptions for demand.
Forecasting sales figures
Sales forecasting refers to the estimation of sales figures of an organisation for a given period. Demand forecasting helps in predicting the sales figures by considering historical sales data and current trends in the market.
Better control
In order to have better control on business activities, it is important to have a proper understanding of cost budgets, profit analysis, which can be achieved through demand forecasting.
Controlling inventory
As discussed earlier, demand forecasting helps in estimating the future demand for an organisation’s products or services. This, in turn, helps the organisation to accurately assess its requirement for raw material, semi-finished goods, spare parts, etc.
Assessing manpower requirement
Demand forecasting helps inaccurate estimation of the manpower required to produce the desired output, thereby avoiding the situations of under-employment or over-employment.
Ensuring stability
Demand forecasting helps an organisation to stabilise their operations by initiating the development of suitable business policies to meet cyclical and seasonal fluctuations of an economy.
Planning import and export policies
At the macro level, demand forecasting serves as an effective tool for the government in determining the import and export policies for the nation. It helps in assessing whether import is required to meet the possible deficit in domestic supply.
Also Read: What is Consumer Demand?
Factors Influencing Demand Forecasting
There are a number of factors that affect the process of demand forecasting. Figure lists down various factors influencing demand forecasting:
- Prevailing Economic Conditions
- Existing conditions of the Industry
- Existing Condition of an Organization
- Prevailing Market Conditions
- Psychological Conditions
- Competitive Conditions
- Import – Export policies

Let us discuss these factors in detail.
Prevailing Economic Conditions
Demand forecasting can be affected by the changing price levels, national and per capita income, consumption pattern of consumers, saving and investment practices, employment level, etc. of an economy.
Thus, it is important that existing economic conditions should be assessed in order to align demand forecasting with current economic trends.
Existing conditions of the Industry
The assessment of demand for an organisation’s products and services is also affected by the overall conditions of the industry in which the organisation operates.
For example, concentration of an industry increases the level of competition, which directly affects the demand for products and services of different organisations in the industry. In such a case, demand forecasted by organisations may falter.
Existing Condition of an Organization
Apart from industry conditions, the internal state of an organisation also affects demand forecasting. Within the organisation, demand forecasting is affected by various factors, such as plant capacity, product quality, product price, advertising and distribution policies, financial policies, etc.
Prevailing Market Conditions
in market conditions, such as change in the prices of goods; change in consumers’ expectations, tastes and preferences; change in the prices of related goods; and change in the income level of consumers also influence the demand for an organisation’s products and services.
Sociological factors, such as size and density of population, age group, size of family, family life cycle, education level, family income, social awareness, etc. largely impact demand forecasts of an organisation. For example, markets having a large population of youngsters would have a higher demand for lifestyle products, electronic gadgets, etc.
Psychological Conditions
Psychological factors, such as changes in consumer attitude, habits, fashion, lifestyle, perception, cultural and religious beliefs, etc. affect demand forecast of an organisation to a large extent.
Competitive Conditions
A market consists of several organisations offering similar products. This gives rise to competition in the market, which affects demand forecasted by organisations.
For example, reduction in trade barriers increases the number of new entrants in a market, which affects the demand for products and services of existing organisations.
Import – Export policies
The demand for export-import goods gets directly affected by changes in factors, such as import and export control, terms and conditions of import and export, import/export policies, import/export conditions, etc.
Also Read: What is Business Cycle?
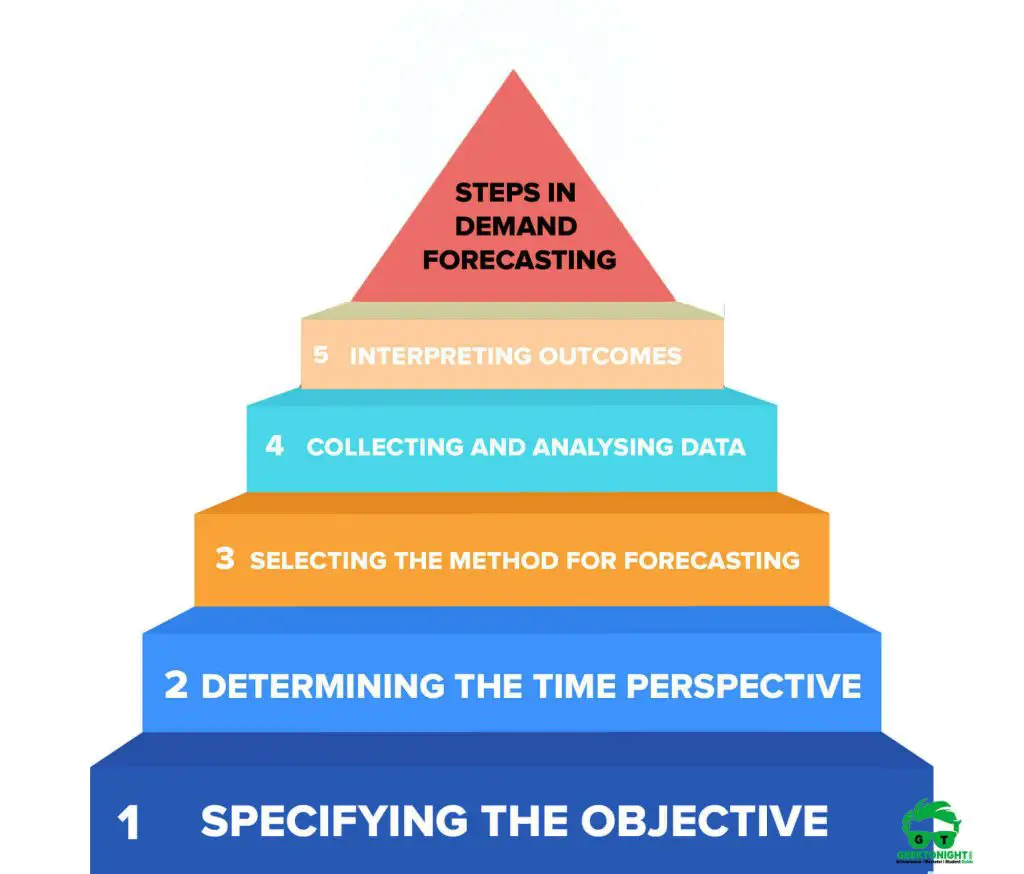
Steps in Demand Forecasting
To achieve the desired results, it is important that demand forecasting is done systematically. Demand forecasting involves a number of steps, which are shown in Figure:
- Specifying the objective
- Determining the time perspective
- Selecting the method for forecasting
- Collecting and analysing data
- Interpreting outcomes
Let us discuss these steps in detail.
Specifying the objective
The purpose of demand forecasting needs to be specified before starting the process. The objective can be specified on the following basis:
- Short-term or long-term demand for a product
- Industry demand or demand specific to an organisation
- Whole market demand or demand specific to a market segment
Determining the time perspective
Depending on the objective, the demand can be forecasted for a short period (2-3 years) or long period (beyond 10 years). If an organisation performs long-term demand forecasting, it needs to take into consideration constant changes in the market as well the economy.
Selecting the method for forecasting
There are various methods of demand forecasting, which have been discussed later in the chapter. However, not all methods are suitable for all types of demand forecasting. Depending on the objective, time period, and availability of data, the organisation needs to select the most suitable forecasting method. The selection of demand forecasting method also depends on the experience and expertise of the demand forecaster.
Collecting and analysing data
After selecting the demand forecasting method, the data needs to be collected. Data can be gathered either from primary sources or secondary sources or both. As data is collected in the raw form, it needs to be analysed in order to derive meaningful information out of it.
Interpreting outcomes
After the data is analysed, it is used to estimate demand for the predetermined years. Generally, the results obtained are in the form of equations, which need to be presented in a comprehensible format.
Also Read: Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
Limitations of Demand Forecasting
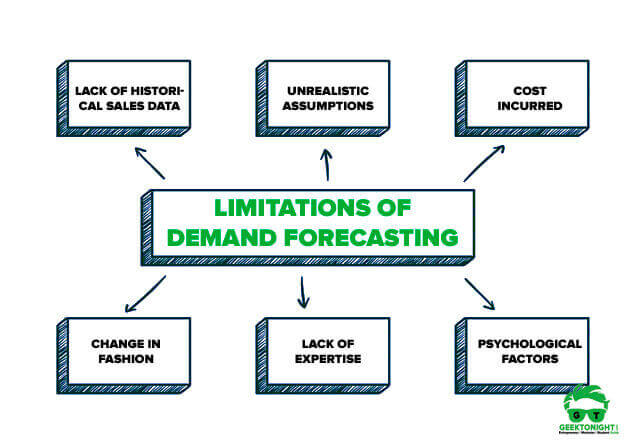
Limitations of Demand Forecasting are:
- Lack of historical sales data
- Unrealistic assumptions
- Cost incurred
- Change in fashion
- Lack of expertise
- Psychological factors
Lack of historical sales data
Past sales figures may not always be available with an organisation. For example, in case of a new commodity, there is unavailability of historical sales data. In such cases, new data is required to be collected for demand forecasting, which can be cumbersome and challenging for an organisation.
Unrealistic assumptions
Demand forecasting is based on various assumptions, which may not always be consistent with the present market conditions. In such a case, relying on these assumptions may produce incorrect forecasts for the future.
Cost incurred
Demand forecasting incurs different costs for an organisation, such as implementation cost, labour cost, and administrative cost. These costs may be very high depending on the complexity of the forecasting method selected and the resources utilised. Owing to limited means, it becomes difficult for new startups and small-scale organisations to perform demand forecasting.
Change in fashion
Consumers’ tastes and preferences continue to change with a change in fashion. This limits the use of demand forecasting as it is generally based on historical trend analysis.
Lack of expertise
Demand forecasting requires effective skills, knowledge and experience of personnel making forecasts. In the absence of trained experts, demand forecasting becomes a challenge for an organisation. This is because if the responsibility of demand forecasting is assigned to untrained personnel, it could bring huge losses to the organisation.
Psychological factors
Consumers usually prefer a particular type of product over others. However, factors, such as fear of war and changes in economic policy, could affect consumers’ psychology. In such cases, the outcomes of forecasting may no longer remain relevant for the time period.
Also Read: Criteria for Good Demand Forecasting
Techniques of Demand Forecasting
Methods of demand forecasting are broadly categorised into two types. Let us discuss these techniques & methods of demand forecasting in detail:
Qualitative Techniques
Quantitative Techniques
- Time Series Analysis
- Smoothing Techniques
- Barometric Methods
- Econometric Methods
Leave a Reply