Law of Supply states that, other factors being constant, quantity supplied increases with a price increase and decreases with a decrease in the price of the commodity. The degree of change in quantity supplied in response to changes in price is known as Price Elasticity of Supply. Price Elasticity of supply undertakes how the supply of a particular product responds to price fluctuations. There are five types of elasticity of supply; Perfectly Elastic Supply, More than Unit Elastic Supply, Unit Elastic Supply, Less than Unit Elastic Supply, and Perfectly Inelastic Supply.
Types of Elasticity of Supply
1. Perfectly Elastic Supply:
Price Elasticity of Supply is said to be perfect elastic supply when at a particular price, there is infinite supply for a commodity, and with even a small change in its price, the supply becomes zero. Perfectly Elastic Supply indicates that the suppliers are willing to sell only when the prices of commodities are high. The price elasticity in this case is infinite; i.e., ES = ∞, and the supply curve is a horizontal straight line parallel to the X-axis.

Quantity supplied can be OQ, OQ1, or OQ2 at the same price as OP.
| Price (in ₹) | Supply (in units) |
|---|---|
| 20 | 150 |
| 20 | 250 |
| 20 | 350 |
The quantity supplied can be 150, 250, or 350 units at the same price of ₹20. However, it must be kept in mind that perfectly inelastic supply is an imaginary situation.
2. More than Unit Elastic Supply/Highly Elastic Supply:
Price Elasticity of Supply is said to be more than unit elastic when the percentage change in supply is relatively greater than the percentage change in price. The price elasticity of supply in such cases is greater than 1, i.e., ES > 1, and the supply curve intercepts on the Y-axis.
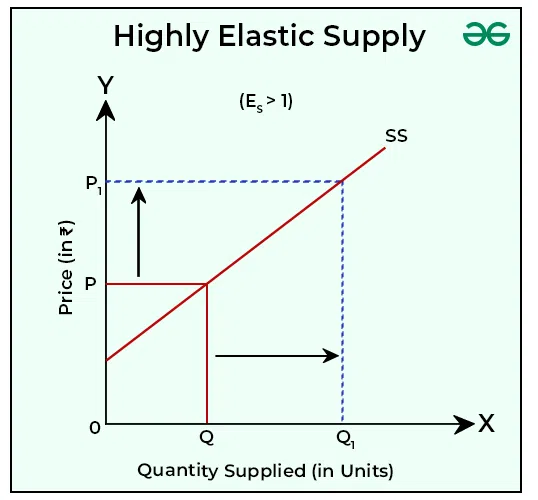
The quantity supplied rises from OQ to OQ1 with a rise in price from OP to OP1. As QQ1 is proportionately more than PP1, the elasticity of supply is more than 1.
| Price (in ₹) | Supply (in units) |
|---|---|
| 20 | 200 |
| 30 | 400 |
The quantity supplied increases by 100% due to a 50% increase in price.
3. Unitary Elastic Supply:
Price Elasticity of Supply is said to be unit elastic supply when a price change is precisely equal to the change in quantity supplied. The price elasticity of supply is 1 in such cases; i.e., ES = 1, and the supply curve is a straight line passing through the origin.

The quantity supplied rises from OQ to OQ1 with a rise in price from OP to OP1. As QQ1 is proportionately equal to PP1, the elasticity of supply is equal to 1.
| Price (in ₹) | Supply (in units) |
|---|---|
| 20 | 200 |
| 30 | 300 |
The quantity supplied rises by 50% due to a 50% increase in price.
4. Less than Unit Elastic Supply/Less Elastic Supply:
Price Elasticity of Supply is said to be less than unit elastic supply when the percentage change in supply is relatively lower than the percentage change in price. Price Elasticity of Supply is less than 1 in such cases; i.e., ES < 1, and the supply curve intercepts on the X-axis.

The quantity supplied rises from OQ to OQ1 with a rise in prices from OP to OP1. As QQ1 is proportionately less than PP1, the elasticity of supply is less than 1.
| Price (in ₹) | Supply (in units) |
|---|---|
| 20 | 200 |
| 30 | 240 |
The quantity supplied rises by 20% due to a 50% increase in price.
5. Perfectly Inelastic Supply:
Price Elasticity of Supply is said to be perfect inelastic supply when the quantity supplied does not change with the change in price. It shows that the supply would remain the same irrespective of the price. The price elasticity in this case is zero; i.e., ES = 0, and the supply curve is a vertical straight line parallel to the Y-axis.

Quantity supplied remains the same at OQ, with the change in price from OP to OP1 to OP2.
| Price (in ₹) | Supply (in units) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 30 |
| 20 | 30 |
| 30 | 30 |
The quantity supplied remains the same at 30 units, whether the price is ₹10, ₹20, or ₹30.
Leave a Reply