Here’s how these tokens work in websites and web apps:
- A web token is returned when a user logs in successfully using their credentials (like email/password).
- Now, whenever the user wants to access a route or a resource on a web app that’s protected, the user agent sends this token in the authorization header such as: Authorization: Bearer token
As you can see, it uses the Bearer schema, which is a cryptic string usually generated by the server in response to a login request.
- Next, the server’s routes will check whether the provided access toke is valid in the Authorization header.
- If it’s valid, the user is allowed to access the requested protected routes.
Here’s a diagram that shows how the access token is obtained from the authorization server in order to access protected routes:
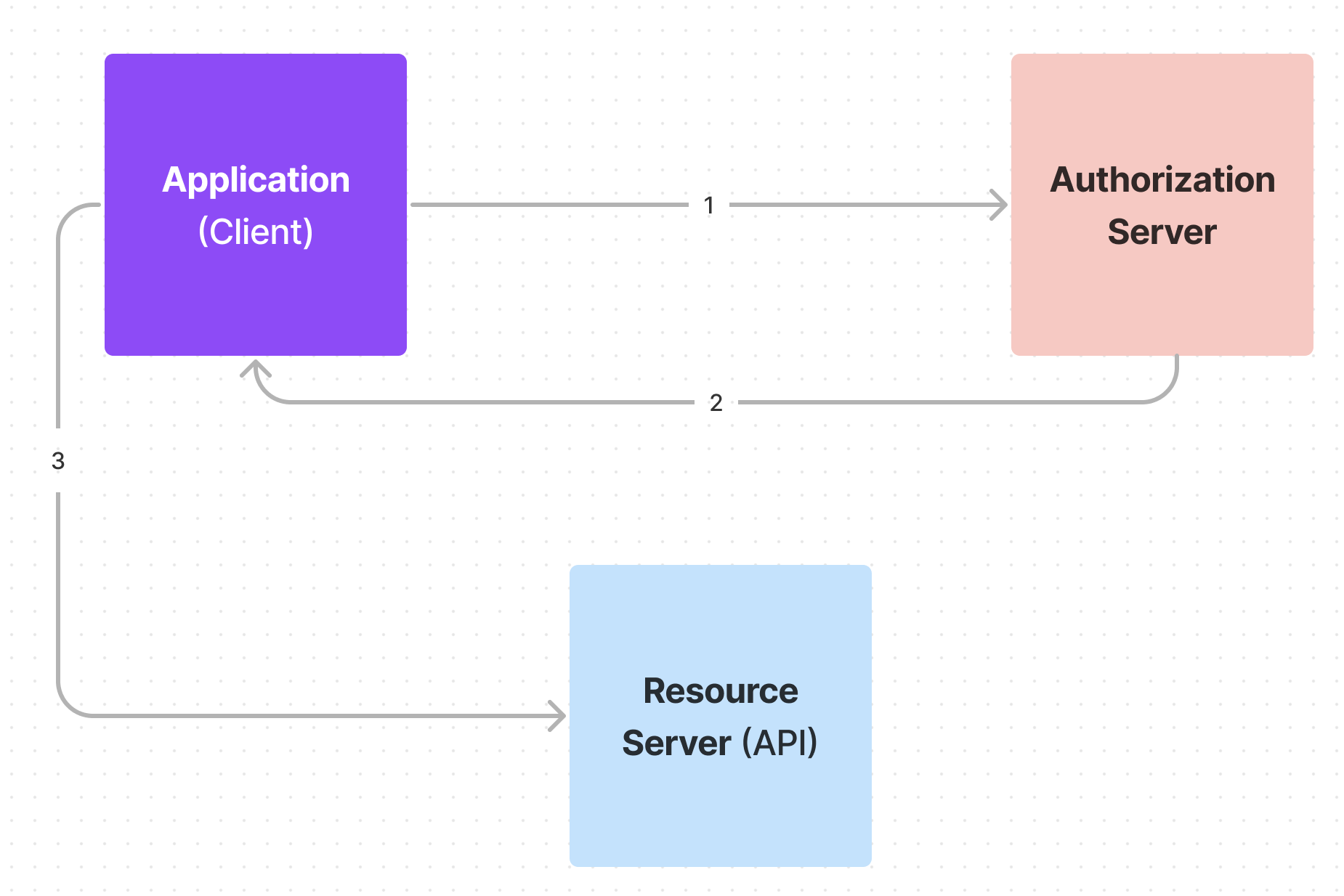
- The client requests for authorization to the authentication server.
- After granting the authorization, the auth server returns an access token to the application.
- The application uses the token to access a protected route via some API.
Now that you know all about what access tokes are, where they’re used, and how they work in a web app, let’s try to take a look at using one of the authentication providers, i.e., Authgear.
Leave a Reply