We must understand the differences between JDK, JRE, and JVM before proceeding further to Java. See the brief overview of JVM here.
If you want to get the detailed knowledge of Java Virtual Machine, move to the next page. Firstly, let’s see the differences between the JDK, JRE, and JVM.
JVM
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is an abstract machine. It is called a virtual machine because it doesn’t physically exist. It is a specification that provides a runtime environment in which Java bytecode can be executed. It can also run those programs which are written in other languages and compiled to Java bytecode.
JVMs are available for many hardware and software platforms. JVM, JRE, and JDK are platform dependent because the configuration of each OS is different from each other. However, Java is platform independent. There are three notions of the JVM: specification, implementation, and instance.
The JVM performs the following main tasks:
- Loads code
- Verifies code
- Executes code
- Provides runtime environment
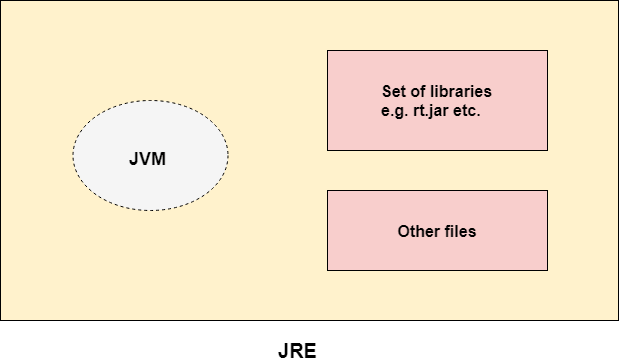
JRE
JRE is an acronym for Java Runtime Environment. It is also written as Java RTE. The Java Runtime Environment is a set of software tools which are used for developing Java applications. It is used to provide the runtime environment. It is the implementation of JVM. It physically exists. It contains a set of libraries + other files that JVM uses at runtime.
The implementation of JVM is also actively released by other companies besides Sun Micro Systems.
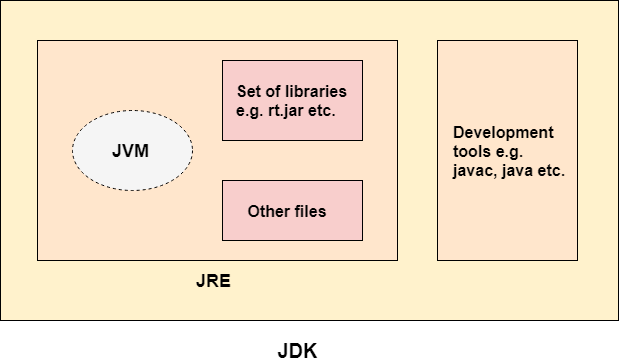
JDK
JDK is an acronym for Java Development Kit. The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a software development environment which is used to develop Java applications and applets. It physically exists. It contains JRE + development tools.
JDK is an implementation of any one of the below given Java Platforms released by Oracle Corporation:
- Standard Edition Java Platform
- Enterprise Edition Java Platform
- Micro Edition Java Platform
The JDK contains a private Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and a few other resources such as an interpreter/loader (java), a compiler (javac), an archiver (jar), a documentation generator (Javadoc), etc. to complete the development of a Java Application.
Leave a Reply