- HTML attributes are special words which provide additional information about the elements or attributes are the modifier of the HTML element.
- Each element or tag can have attributes, which defines the behaviour of that element.
- Attributes should always be applied with start tag.
- The Attribute should always be applied with its name and value pair.
- The Attributes name and values are case sensitive, and it is recommended by W3C that it should be written in Lowercase only.
- You can add multiple attributes in one HTML element, but need to give space between two attributes.
Syntax
<element attribute_name="value">content</element> Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
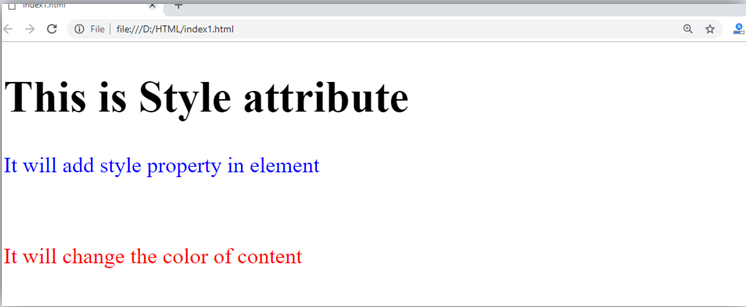
<h1> This is Style attribute</h1>
<p style="height: 50px; color: blue">It will add style property in element</p>
<p style="color: red">It will change the color of content</p>
</body>
</html>Output:
Explanation of above example:
<p style="height: 50px; color: blue">It will add style property in element</p>
In the above statement, we have used paragraph tags in which we have applied style attribute. This attribute is used for applying CSS property on any HTML element. It provides height to paragraph element of 50px and turns it colour to blue.
<p style="color: red">It will change the color of content</p> In the above statement we have again used style attribute in paragraph tag, which turns its colour red.
Note: There are some commonly used attributes are given below, and the complete list and explanation of all attributes are given in HTML attributes List.
The title attribute in HTML
Description: The title attribute is used as text tooltip in most of the browsers. It display its text when user move the cursor over a link or any text. You can use it with any text or link to show the description about that link or text. In our example, we are taking this with paragraph tag and heading tag.
Example
With <h1> tag:<h1 title="This is heading tag">Example of title attribute</h1> With <p> tag:<p title="This is paragraph tag">Move the cursor over the heading and paragraph, and you will see a description as a tooltip</p> Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
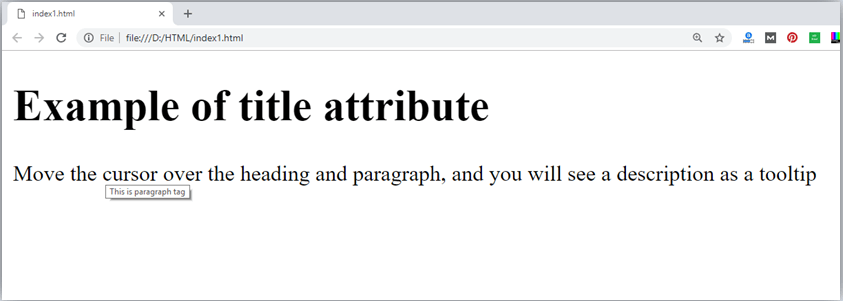
<h1 title="This is heading tag">Example of title attribute</h1>
<p title="This is paragraph tag">Move the cursor over the heading and paragraph, and you will see a description as a tooltip</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:
The href attribute in HTML
Description: The href attribute is the main attribute of <a> anchor tag. This attribute gives the link address which is specified in that link. The href attribute provides the hyperlink, and if it is blank, then it will remain in same page.
Example
With link address:
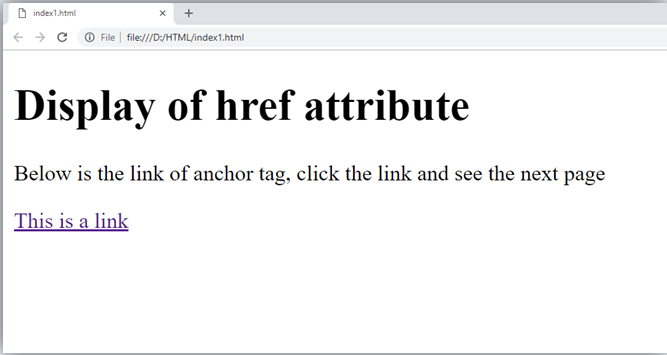
<a href="https://www.javatpoint.com/html-anchor">This is a link</a> Without link address:
<a href="">This is a link</a>
The src Attribute
The src attribute is one of the important and required attribute of <img> element. It is source for the image which is required to display on browser. This attribute can contain image in same directory or another directory. The image name or source should be correct else browser will not display the image.
Example
<img src="whitepeacock.jpg" height="400" width="600"> Note: The above example also have height and width attribute, which define the height and width of image on web page.
Output:
Quotes: single quotes or double quotes?
In this chapter you have seen that, we have used attribute with double quotes, but some people might use single quotes in HTML. So use of single quotes with HTML attribute, is also allowed. The following both statements are absolutely fine.
<a href="https://www.javatpoint.com">A link to HTML.</a>
<a href='https://www.javatpoint.com'>A link to HTML.</a>IN HTML5, you can also omit use of quotes around attribute values.
<a href=https://www.foobrdigital.com>A link to HTML.</a>
Leave a Reply