What is Demand Function?
Demand function represents the relationship between the quantity demanded for a commodity (dependent variable) and the price of the commodity (independent variable).
Table of Content [Show]
Demand Function Formula
Mathematically, a function is a symbolic representation of the relationship between dependent and independent variables.
Let us assume that the quantity demanded of a commodity X is Dx, which depends only on its price Px, while other factors are constant. It can be mathematically represented as:
Dx = f (Px)
However, the quantitative relationship between Dx and Px is expressed as:
Dx = a – bPx
Where a (intercept) and b (relationship between Dx and Px) are constants.
Also Read: Law of Demand
Types of Demand Function
2 types of demand function are:
Linear demand function
In the linear demand function, the slope of the demand curve remains constant throughout its length. A linear demand equation is mathematically expressed as:
Dx = a – bPx
In this equation, a denotes the total demand at zero price.
b = slope or the relationship between Dx and Px
b can also be denoted by change in Dx for change in Px
If the values of a and b are known, the demand for a commodity at any given price can be computed using the equation given above.
For example, let us assume a = 50, b = 2.5, and Px= 10:
Demand function is:
Dx = 50 – 2.5 (Px)
Therefore, Dx = 50 – 2.5 (10)
or Dx= 25 units
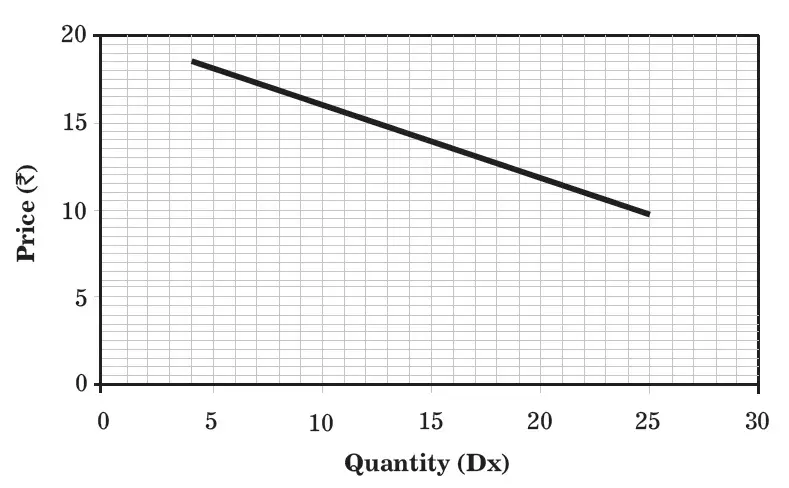
The demand schedule for the above function is given in Table
| QUANTITY DEMANDED OF COMMODITY X | PRICE LEVELS OF COMMODITY X |
|---|---|
| 5 | 18 |
| 10 | 16 |
| 15 | 14 |
| 20 | 12 |
When the demand schedule is plotted on a graph, it produces a linear demand curve, which is shown in Figure below.
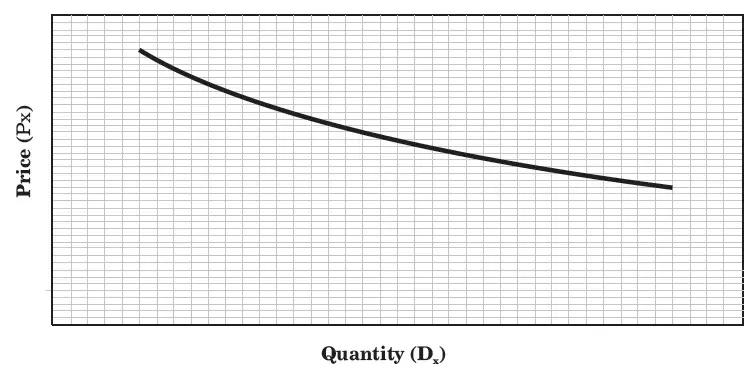
Non linear demand function
In the non linear or curvilinear demand function, the slope of the demand curve (ΔP/ΔQ) changes along the demand curve. Instead of a demand line, non-linear demand function yields a demand curve.
A non-linear demand equation is mathematically expressed as:
Dx = a (Px)-b
Or of a rectangular hyperbola of the form
Dx = (a/Px + c) b
where a, b, c> 0
Exponent –b of price in the non-linear demand function refers to the coefficient of the price elasticity of demand.
Figure, represents a non-linear demand function:
Leave a Reply