In this section, we will learn how to implements Redux in React application. Here, we provide a simple example to connect Redux and React.
Step-1 Create a new react project using create-react-app command. I choose the project name: “reactproject.” Now, install Redux and React-Redux.
javatpoint@root:~/Desktop$ npx create-react-app reactproject
javatpoint@root:~/Desktop/reactproject$ npm install redux react-redux --save Step-2 Create Files and Folders
In this step, we need to create folders and files for actions, reducers, components, and containers. After creating folders and files, our project looks like as below image.
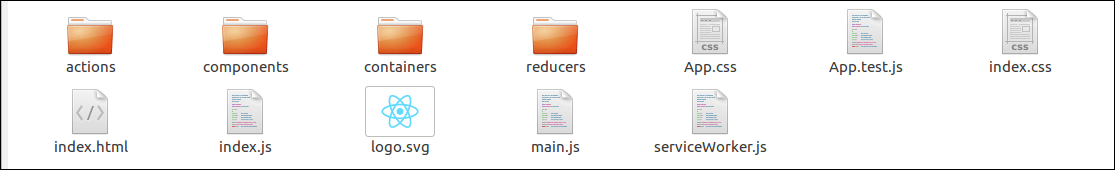
Step-3 Actions
It uses ‘type‘ property to inform about data that should be sent to the Store. In this folder, we will create two files: index.js and index.spec.js. Here, we have created an action creator that returns our action and sets an id for every created item.
Index.js
let nextTodoId = 0
export const addTodo = text => ({
type: 'ADD_TODO',
id: nextTodoId++,
text
})
export const setVisibilityFilter = filter => ({
type: 'SET_VISIBILITY_FILTER',
filter
})
export const toggleTodo = id => ({
type: 'TOGGLE_TODO',
id
})
export const VisibilityFilters = {
SHOW_ALL: 'SHOW_ALL',
SHOW_COMPLETED: 'SHOW_COMPLETED',
SHOW_ACTIVE: 'SHOW_ACTIVE'
} import * as actions from './index'
describe('todo actions', () => {
it('addTodo should create ADD_TODO action', () => {
expect(actions.addTodo('Use Redux')).toEqual({
type: 'ADD_TODO',
id: 0,
text: 'Use Redux'
})
})
it('setVisibilityFilter should create SET_VISIBILITY_FILTER action', () => {
expect(actions.setVisibilityFilter('active')).toEqual({
type: 'SET_VISIBILITY_FILTER',
filter: 'active'
})
})
it('toggleTodo should create TOGGLE_TODO action', () => {
expect(actions.toggleTodo(1)).toEqual({
type: 'TOGGLE_TODO',
id: 1
})
})
})Step-4 Reducers
As we know, Actions only trigger changes in the app, and the Reducers specify those changes. The Reducer is a function which takes two parameters ‘Action’ and ‘State’ to calculate and return an updated State. It read the payloads from the ‘Actions’ and then updates the ‘Store’ via the State accordingly.
In the given files, each Reducer managing its own part of the global State. The State parameter is different for every Reducer and corresponds to the part of the ‘State’ it manages. When the app becomes larger, we can split the Reducers into separate files and keep them completely independent and managing different data domains.
Here, we are using ‘combineReducers’ helper function to add any new Reducers we might use in the future.
index.js
import { combineReducers } from 'redux'
import todos from './todos'
import visibilityFilter from './visibilityFilter'
export default combineReducers({
todos,
visibilityFilter
}) Todos.js
const todos = (state = [], action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'ADD_TODO':
return [
...state,
{
id: action.id,
text: action.text,
completed: false
}
]
case 'TOGGLE_TODO':
return state.map(todo =>
(todo.id === action.id)
? {...todo, completed: !todo.completed}
: todo
)
default:
return state
}
}
export default todos Todos.spec.js
import todos from './todos'
describe('todos reducer', () => {
it('should handle initial state', () => {
expect(
todos(undefined, {})
).toEqual([])
})
it('should handle ADD_TODO', () => {
expect(
todos([], {
type: 'ADD_TODO',
text: 'Run the tests',
id: 0
})
).toEqual([
{
text: 'Run the tests',
completed: false,
id: 0
}
])
expect(
todos([
{
text: 'Run the tests',
completed: false,
id: 0
}
], {
type: 'ADD_TODO',
text: 'Use Redux',
id: 1
})
).toEqual([
{
text: 'Run the tests',
completed: false,
id: 0
}, {
text: 'Use Redux',
completed: false,
id: 1
}
])
expect(
todos([
{
text: 'Run the tests',
completed: false,
id: 0
}, {
text: 'Use Redux',
completed: false,
id: 1
}
], {
type: 'ADD_TODO',
text: 'Fix the tests',
id: 2
})
).toEqual([
{
text: 'Run the tests',
completed: false,
id: 0
}, {
text: 'Use Redux',
completed: false,
id: 1
}, {
text: 'Fix the tests',
completed: false,
id: 2
}
])
})
it('should handle TOGGLE_TODO', () => {
expect(
todos([
{
text: 'Run the tests',
completed: false,
id: 1
}, {
text: 'Use Redux',
completed: false,
id: 0
}
], {
type: 'TOGGLE_TODO',
id: 1
})
).toEqual([
{
text: 'Run the tests',
completed: true,
id: 1
}, {
text: 'Use Redux',
completed: false,
id: 0
}
])
})
}) VisibilityFilter.js
import { VisibilityFilters } from '../actions'
const visibilityFilter = (state = VisibilityFilters.SHOW_ALL, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'SET_VISIBILITY_FILTER':
return action.filter
default:
return state
}
}
export default visibilityFilter Step-5 Components
It is a Presentational Component, which concerned with how things look such as markup, styles. It receives data and invokes callbacks exclusively via props. It does not know where the data comes from or how to change it. It only renders what is given to them.
App.js
It is the root component which renders everything in the UI.
import React from 'react'
import Footer from './Footer'
import AddTodo from '../containers/AddTodo'
import VisibleTodoList from '../containers/VisibleTodoList'
const App = () => (
<div>
<AddTodo />
<VisibleTodoList />
<Footer />
</div>
)
export default App Footer.js
It tells where the user changes currently visible todos.
import React from 'react'
import FilterLink from '../containers/FilterLink'
import { VisibilityFilters } from '../actions'
const Footer = () => (
<p>
Show: <FilterLink filter={VisibilityFilters.SHOW_ALL}>All</FilterLink>
{', '}
<FilterLink filter={VisibilityFilters.SHOW_ACTIVE}>Active</FilterLink>
{', '}
<FilterLink filter={VisibilityFilters.SHOW_COMPLETED}>Completed</FilterLink>
</p>
)
export default Footer Link.js
It is a link with a callback.
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
const Link = ({ active, children, onClick }) => {
if (active) {
return <span>{children}</span>
}
return (
<a
href=""
onClick={e => {
e.preventDefault()
onClick()
}}
>
{children}
</a>
)
}
Link.propTypes = {
active: PropTypes.bool.isRequired,
children: PropTypes.node.isRequired,
onClick: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
export default Link Todo.js
It represents a single todo item which shows text.
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
const Todo = ({ onClick, completed, text }) => (
<li
onClick={onClick}
style={{
textDecoration: completed ? 'line-through' : 'none'
}}
>
{text}
</li>
)
Todo.propTypes = {
onClick: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
completed: PropTypes.bool.isRequired,
text: PropTypes.string.isRequired
}
export default Todo TodoList.js
It is a list to show visible todos{ id, text, completed }.
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
import Todo from './Todo'
const TodoList = ({ todos, onTodoClick }) => (
<ul>
{todos.map((todo, index) => (
<Todo key={index} {...todo} onClick={() => onTodoClick(index)} />
))}
</ul>
)
TodoList.propTypes = {
todos: PropTypes.arrayOf(
PropTypes.shape({
id: PropTypes.number.isRequired,
completed: PropTypes.bool.isRequired,
text: PropTypes.string.isRequired
}).isRequired
).isRequired,
onTodoClick: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
export default TodoList Step-6 Containers
It is a Container Component which concerned with how things work such as data fetching, updates State. It provides data and behavior to presentational components or other container components. It uses Redux State to read data and dispatch Redux Action for updating data.
AddTodo.js
It contains the input field with an ADD (submit) button.
import React from 'react'
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
import { addTodo } from '../actions'
const AddTodo = ({ dispatch }) => {
let input
return (
<div>
<form onSubmit={e => {
e.preventDefault()
if (!input.value.trim()) {
return
}
dispatch(addTodo(input.value))
input.value = ''
}}>
<input ref={node => input = node} />
<button type="submit">
Add Todo
</button>
</form>
</div>
)
}
export default connect()(AddTodo) FilterLink.js
It represents the current visibility filter and renders a link.
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
import { setVisibilityFilter } from '../actions'
import Link from '../components/Link'
const mapStateToProps = (state, ownProps) => ({
active: ownProps.filter === state.visibilityFilter
})
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch, ownProps) => ({
onClick: () => dispatch(setVisibilityFilter(ownProps.filter))
})
export default connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(Link) VisibleTodoList.js
It filters the todos and renders a TodoList.
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
import { toggleTodo } from '../actions'
import TodoList from '../components/TodoList'
import { VisibilityFilters } from '../actions'
const getVisibleTodos = (todos, filter) => {
switch (filter) {
case VisibilityFilters.SHOW_ALL:
return todos
case VisibilityFilters.SHOW_COMPLETED:
return todos.filter(t => t.completed)
case VisibilityFilters.SHOW_ACTIVE:
return todos.filter(t => !t.completed)
default:
throw new Error('Unknown filter: ' + filter)
}
}
const mapStateToProps = state => ({
todos: getVisibleTodos(state.todos, state.visibilityFilter)
})
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
toggleTodo: id => dispatch(toggleTodo(id))
})
export default connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(TodoList) Step-7 Store
All container components need access to the Redux Store to subscribe to it. For this, we need to pass it(store) as a prop to every container component. However, it gets tedious. So we recommend using special React Redux component called which make the store available to all container components without passing it explicitly. It used once when you render the root component.
index.js
import React from 'react'
import { render } from 'react-dom'
import { createStore } from 'redux'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import App from './components/App'
import rootReducer from './reducers'
const store = createStore(rootReducer)
render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>,
document.getElementById('root')
) Output
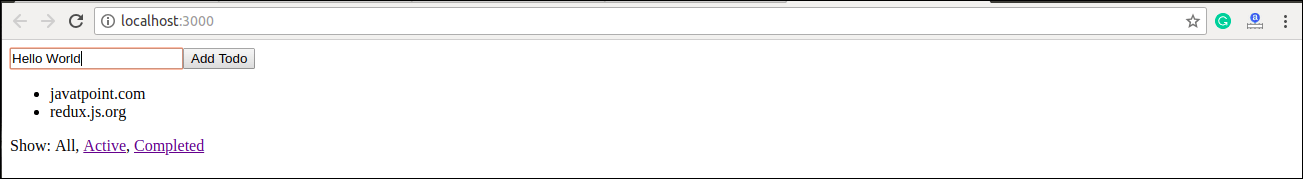
When we execute the application, it gives the output as below screen.

Now, we will be able to add items in the list.
Leave a Reply