A map is a data collection type where data is stored in the form of pairs. It contains a unique key. The value stored in the map must be mapped to the key. We cannot store a duplicate pair in the map(). It is because of the uniqueness of each stored key. It is mainly used for fast searching and looking up data.
In React, the ?map? method used to traverse and display a list of similar objects of a component. A map is not the feature of React. Instead, it is the standard JavaScript function that could be called on any array. The map() method creates a new array by calling a provided function on every element in the calling array.
Example
In the given example, the map() function takes an array of numbers and double their values. We assign the new array returned by map() to the variable doubleValue and log it.
var numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const doubleValue = numbers.map((number)=>{
return (number * 2);
});
console.log(doubleValue); In React, the map() method used for:
1. Traversing the list element.
Example
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
function NameList(props) {
const myLists = props.myLists;
const listItems = myLists.map((myList) =>
<li>{myList}</li>
);
return (
<div>
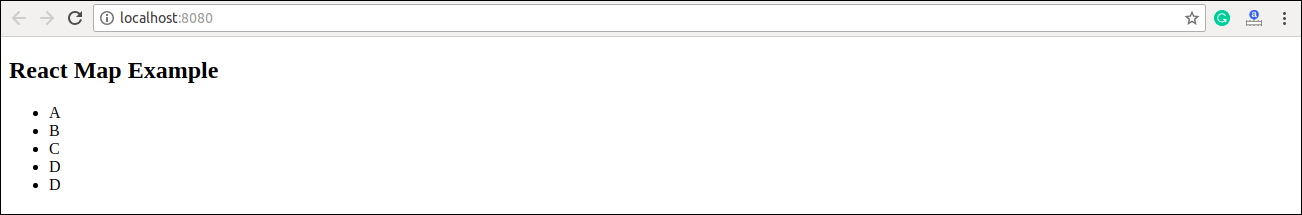
<h2>React Map Example</h2>
<ul>{listItems}</ul>
</div>
);
}
const myLists = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'D'];
ReactDOM.render(
<NameList myLists={myLists} />,
document.getElementById('app')
);
export default App; Output
2. Traversing the list element with keys.
Example
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
function ListItem(props) {
return <li>{props.value}</li>;
}
function NumberList(props) {
const numbers = props.numbers;
const listItems = numbers.map((number) =>
<ListItem key={number.toString()}
value={number} />
);
return (
<div>
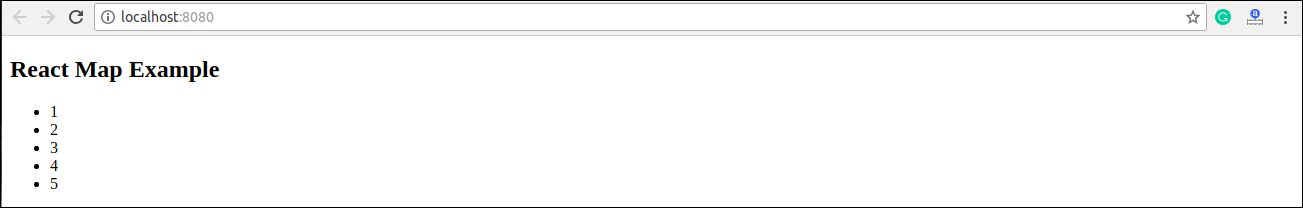
<h2>React Map Example</h2>
<ul> {listItems} </ul>
</div>
);
}
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
ReactDOM.render(
<NumberList numbers={numbers} />,
document.getElementById('app')
);
export default App; Output
Leave a Reply