CSS in React is used to style the React App or Component. The style attribute is the most used attribute for styling in React applications, which adds dynamically-computed styles at render time. It accepts a JavaScript object in camelCased properties rather than a CSS string. There are many ways available to add styling to your React App or Component with CSS. Here, we are going to discuss mainly four ways to style React Components, which are given below:
- Inline Styling
- CSS Stylesheet
- CSS Module
- Styled Components
1. Inline Styling
The inline styles are specified with a JavaScript object in camelCase version of the style name. Its value is the style?s value, which we usually take in a string.
Example
App.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
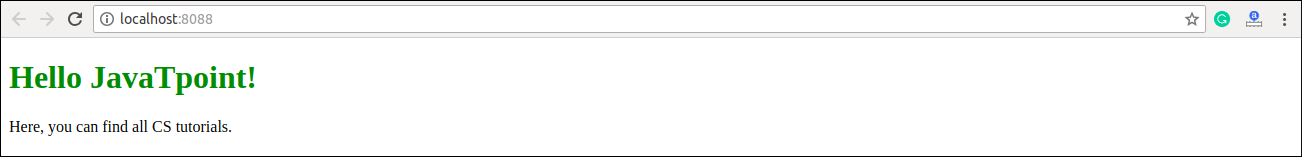
<h1 style={{color: "Green"}}>Hello JavaTpoint!</h1>
<p>Here, you can find all CS tutorials.</p>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App; Note: You can see in the above example, we have used two curly braces in:
<h1 style={{color: “Green”}}>Hello JavaTpoint!</h1>.
It is because, in JSX, JavaScript expressions are written inside curly braces, and JavaScript objects also use curly braces, so the above styling is written inside two sets of curly braces {{}}.
Output
camelCase Property Name
If the properties have two names, like background-color, it must be written in camel case syntax.
Example
App.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
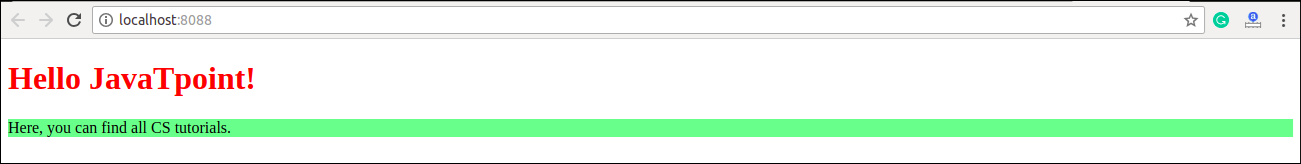
<h1 style={{color: "Red"}}>Hello JavaTpoint!</h1>
<p style={{backgroundColor: "lightgreen"}}>Here, you can find all CS tutorials.</p>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App; Output
Using JavaScript Object
The inline styling also allows us to create an object with styling information and refer it in the style attribute.
Example
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
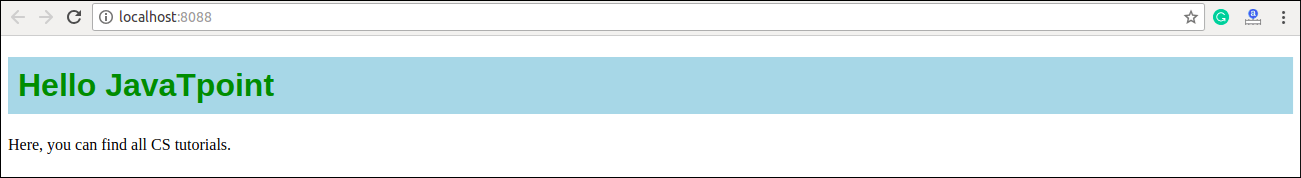
const mystyle = {
color: "Green",
backgroundColor: "lightBlue",
padding: "10px",
fontFamily: "Arial"
};
return (
<div>
<h1 style={mystyle}>Hello JavaTpoint</h1>
<p>Here, you can find all CS tutorials.</p>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;Output
2. CSS Stylesheet
You can write styling in a separate file for your React application, and save the file with a .css extension. Now, you can import this file in your application.
Example
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import './App.css';
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello JavaTpoint</h1>
<p>Here, you can find all CS tutorials.</p>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;App.css
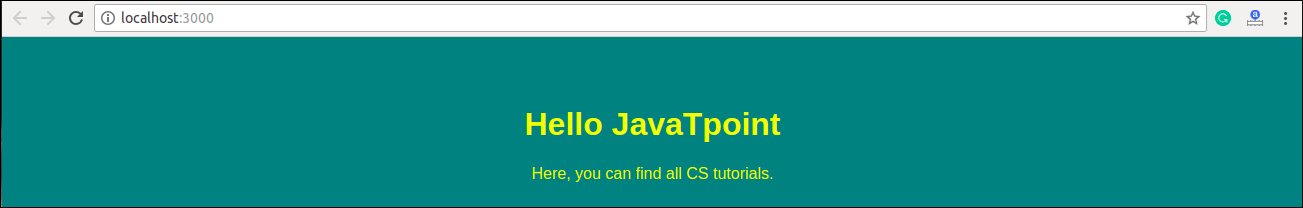
body {
background-color: #008080;
color: yellow;
padding: 40px;
font-family: Arial;
text-align: center;
} Index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<title>React App</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
</body>
</html> Output
3. CSS Module
CSS Module is another way of adding styles to your application. It is a CSS file where all class names and animation names are scoped locally by default. It is available only for the component which imports it, means any styling you add can never be applied to other components without your permission, and you never need to worry about name conflicts. You can create CSS Module with the .module.css extension like a myStyles.module.css name.
Example
App.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import styles from './myStyles.module.css';
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
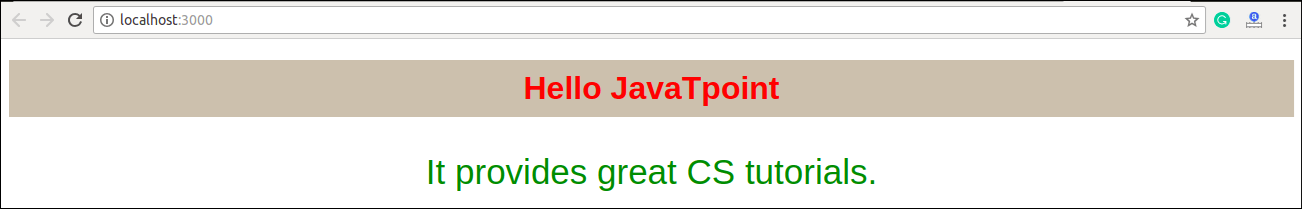
<h1 className={styles.mystyle}>Hello JavaTpoint</h1>
<p className={styles.parastyle}>It provides great CS tutorials.</p>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App; myStyles.module.css
.mystyle {
background-color: #cdc0b0;
color: Red;
padding: 10px;
font-family: Arial;
text-align: center;
}
.parastyle{
color: Green;
font-family: Arial;
font-size: 35px;
text-align: center;
} Output
4. Styled Components
Styled-components is a library for React. It uses enhance CSS for styling React component systems in your application, which is written with a mixture of JavaScript and CSS.
The styled-components provides:
- Automatic critical CSS
- No class name bugs
- Easier deletion of CSS
- Simple dynamic styling
- Painless maintenance
Installation
The styled-components library takes a single command to install in your React application. which is:
$ npm install styled-components --save Example
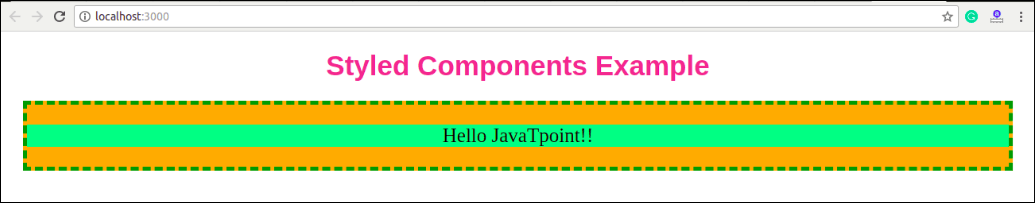
Here, we create a variable by selecting a particular HTML element such as <div>, <Title>, and <paragraph> where we store our style attributes. Now we can use the name of our variable as a wrapper <Div></Div> kind of React component.
App.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import styled from 'styled-components';
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
const Div:any = styled.div`
margin: 20px;
border: 5px dashed green;
&:hover {
background-color: ${(props:any) => props.hoverColor};
}
`;
const Title = styled.h1`
font-family: Arial;
font-size: 35px;
text-align: center;
color: palevioletred;
`;
const Paragraph = styled.p`
font-size: 25px;
text-align: center;
background-Color: lightgreen;
`;
return (
<div>
<Title>Styled Components Example</Title>
<p></p>
<Div hoverColor="Orange">
<Paragraph>Hello JavaTpoint!!</Paragraph>
</Div>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App; Output
Now, execute the App.js file, we will get the output as shown below.

When we move the mouse pointer over the image, its color will be changed, as shown in the below image.
Leave a Reply