Factors Affecting Price Elasticity of Demand
As discussed earlier, the price elasticity of demand of a product reflects the change in the quantity demanded as a result of a change in price. However, the price elasticity differs for different products as it depends on various factors.
Table of Content [Show]
Some of these factors affecting price elasticity of demand are mentioned below:
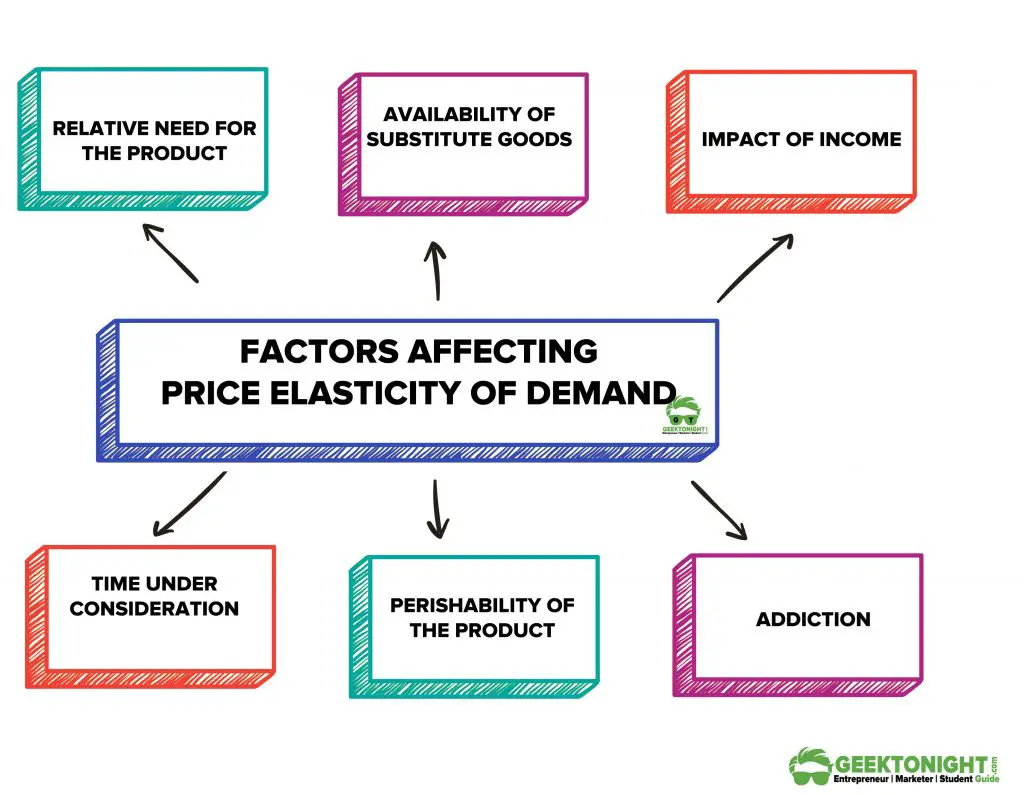
Factors Affecting Price Elasticity of Demand
- Relative need for the product
- Availability of substitute goods
- Impact of income
- Time under consideration
- Perishability of the product
- Addiction
Relative need for the product
The need of every individual is not the same for the same product. A product that is luxury for an individual may be a necessity for another person.
For example, a laptop may be a luxury product for an ordinary individual, while a necessity for a computer engineer. Thus, price elasticity differs across people due to their different needs.
Availability of substitute goods
As discussed in the previous chapters, the availability of substitutes has major impact on the demand for a product. If substitutes are easily available at relatively low prices, the demand for the product would be more elastic and vice versa.
For example, if the price of tea rises, people may opt for coffee.
Impact of income
The amount of income that consumers spend on purchasing a particular product also influences the price elasticity of demand. If consumers spend a large sum on a product, the demand for the product would be elastic.
For example, if the price of salt is raised by 50%, the demand would still be inelastic as consumers would keep on purchasing. Conversely, if the price of a home theatre system is raised by 25%, the demand for the system would be more elastic.
Time under consideration
It majorly influences the price elasticity of demand. Demand for a product remains inelastic in the short run due to failure to postpone demand.
For example, if the price of electricity goes up, people may find it difficult to cut its consumption; thus, the demand would remain less elastic. However, in case of a continuous increase in the price, people would gradually reduce the consumption of electricity by finding various ways, such as using CFL bulbs. In such a case, the demand would be more elastic.
Perishability of the product
If products are perishable in nature, the demand for such products would be inelastic as their consumption cannot be postponed.
For example, if the prices of vegetables that are used regularly are raised, the consumption would not decrease. Thus, the demand would be inelastic. Similarly, if products such as medicines are to be used in an emergency, the demand for them would not decrease.
Addiction
Some products, such as cigarettes and other tobacco-based products, have inelastic demand.
For instance, smokers may be willing to pay extra for cigarettes even in case of a price rise. Thus, the demand would remain the same.
Leave a Reply