What is Contraction in Demand?
When there is a fall in the quantity demanded of a commodity because of an increase in its price by keeping other factors constant, it is known as Contraction in Demand. In simple terms, the demand for a commodity fall because of an increase in its price. Contraction in demand results in an upward movement along the same demand curve.
Example:

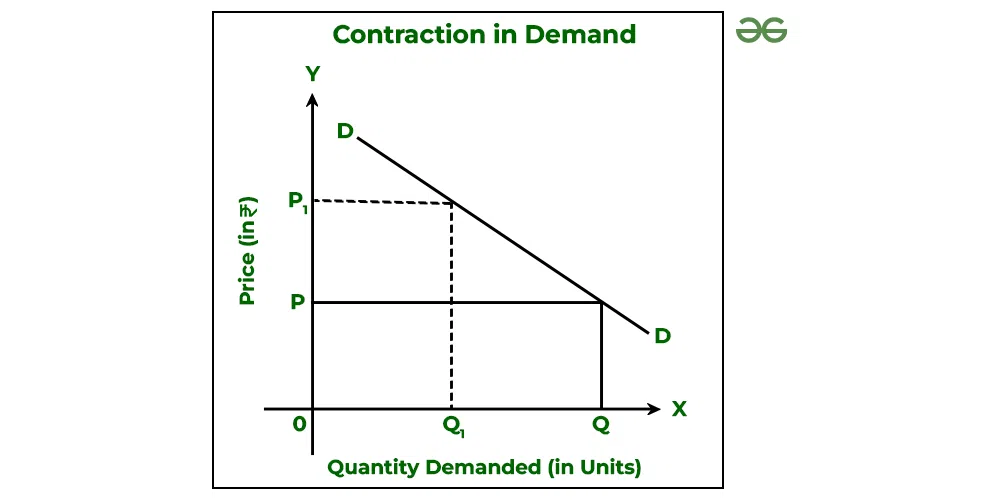
What is Decrease in Demand?
When there is a fall in the quantity demanded of a commodity because of any factor other than the price of the commodity, it is known as Decrease in Demand. In simple terms, the demand for a commodity decreases at the same price, because of changes in other factors. A decrease in demand results in a leftward shift in the demand curve.
Example:


Difference between Contraction in Demand and Decrease in Demand

| Basis | Contraction in Demand | Decrease in Demand |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A fall in the quantity demanded of a commodity because of an increase in its price by keeping other factors constant is known as Contraction in Demand. | A fall in the quantity demanded of a commodity because of any factor other than the price of the commodity is known as Decrease in Demand. |
| Effect on Demand Curve | The effect of contraction in demand is an upward movement along the same demand curve. | The effect of decrease in demand is a leftward shift in the demand curve. |
| Price Effect | There is a negative price effect; i.e., the demand for a commodity decreases when its price rises. | There is no price effect; i.e., the demand for a commodity decreases at the same price. |
| Reason | The demand for a commodity contracts because of an increase in its price. | The demand for a commodity decreases because of an unfavourable change in other factors such as increase in the price of complementary goods, decrease in the price of substitutes, etc. |
| Example | If the demand for a commodity X falls from 200 units to 140 units because of an increase in its price from ₹15 to ₹20, then it is a case of Contraction in Demand. | If the demand for a commodity X falls from 200 units to 140 units with constant price of ₹15 because of changes in other factors like decrease in the price of the substitute good, then it is a case of Decrease in Demand. |
Leave a Reply