
Connecting a method call to the method body is known as binding.
There are two types of binding
- Static Binding (also known as Early Binding).
- Dynamic Binding (also known as Late Binding).
Understanding Type
Let’s understand the type of instance.
1) variables have a type
Each variable has a type, it may be primitive and non-primitive.
int data=30; Here data variable is a type of int.
2) References have a type
class Dog{
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog d1;//Here d1 is a type of Dog
}
}3) Objects have a type
| An object is an instance of particular java class,but it is also an instance of its superclass. |
class Animal{}
class Dog extends Animal{
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog d1=new Dog();
}
}| Here d1 is an instance of Dog class, but it is also an instance of Animal. |
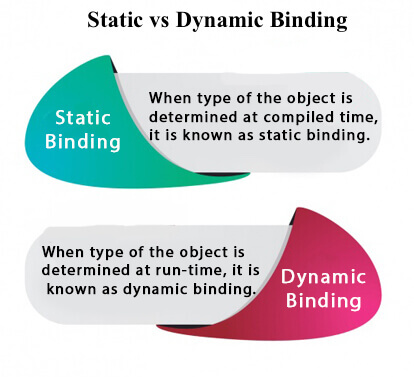
static binding
When type of the object is determined at compiled time(by the compiler), it is known as static binding.
If there is any private, final or static method in a class, there is static binding.
Example of static binding
class Dog{
private void eat(){System.out.println("dog is eating...");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog d1=new Dog();
d1.eat();
}
}Dynamic binding
When type of the object is determined at run-time, it is known as dynamic binding.
Example of dynamic binding
class Animal{
void eat(){System.out.println("animal is eating...");}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
void eat(){System.out.println("dog is eating...");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Animal a=new Dog();
a.eat();
}
}Output:dog is eating...
Leave a Reply