If subclass (child class) has the same method as declared in the parent class, it is known as method overriding in Java.
In other words, If a subclass provides the specific implementation of the method that has been declared by one of its parent class, it is known as method overriding.
Usage of Java Method Overriding
- Method overriding is used to provide the specific implementation of a method which is already provided by its superclass.
- Method overriding is used for runtime polymorphism
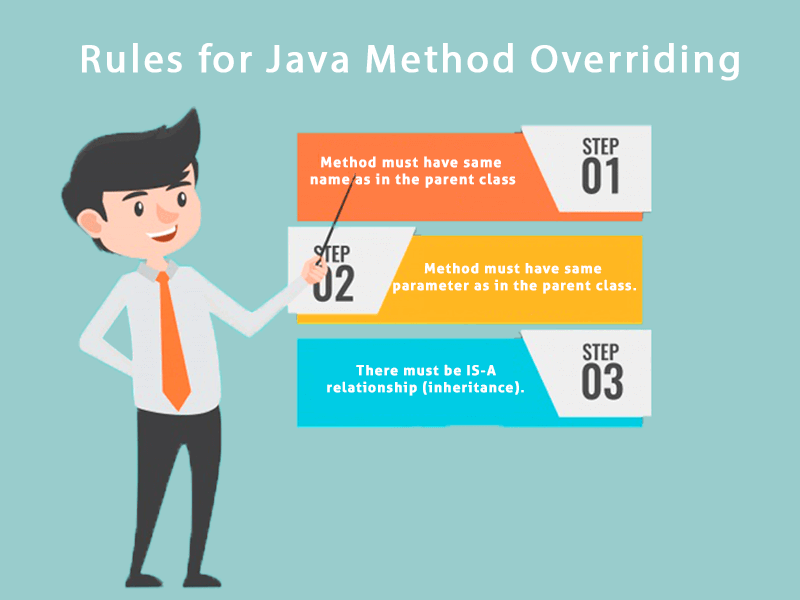
Rules for Java Method Overriding
- The method must have the same name as in the parent class
- The method must have the same parameter as in the parent class.
- There must be an IS-A relationship (inheritance).
Understanding the problem without method overriding
Let’s understand the problem that we may face in the program if we don’t use method overriding.
//Java Program to demonstrate why we need method overriding
//Here, we are calling the method of parent class with child
//class object.
//Creating a parent class
class Vehicle{
void run(){System.out.println("Vehicle is running");}
}
//Creating a child class
class Bike extends Vehicle{
public static void main(String args[]){
//creating an instance of child class
Bike obj = new Bike();
//calling the method with child class instance
obj.run();
}
}Output:
Vehicle is running
Problem is that I have to provide a specific implementation of run() method in subclass that is why we use method overriding.
Example of method overriding
In this example, we have defined the run method in the subclass as defined in the parent class but it has some specific implementation. The name and parameter of the method are the same, and there is IS-A relationship between the classes, so there is method overriding.
//Java Program to illustrate the use of Java Method Overriding
//Creating a parent class.
class Vehicle{
//defining a method
void run(){System.out.println("Vehicle is running");}
}
//Creating a child class
class Bike2 extends Vehicle{
//defining the same method as in the parent class
void run(){System.out.println("Bike is running safely");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike2 obj = new Bike2();//creating object
obj.run();//calling method
}
}Output:
Bike is running safely
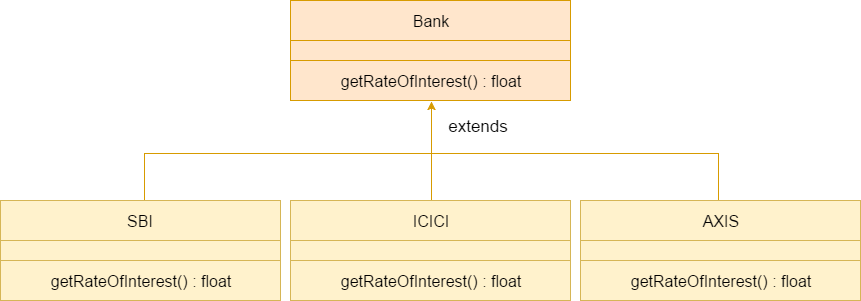
A real example of Java Method Overriding
Consider a scenario where Bank is a class that provides functionality to get the rate of interest. However, the rate of interest varies according to banks. For example, SBI, ICICI and AXIS banks could provide 8%, 7%, and 9% rate of interest.
Java method overriding is mostly used in Runtime Polymorphism which we will learn in next pages.
//Java Program to demonstrate the real scenario of Java Method Overriding
//where three classes are overriding the method of a parent class.
//Creating a parent class.
class Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){return 0;}
}
//Creating child classes.
class SBI extends Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){return 8;}
}
class ICICI extends Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){return 7;}
}
class AXIS extends Bank{
int getRateOfInterest(){return 9;}
}
//Test class to create objects and call the methods
class Test2{
public static void main(String args[]){
SBI s=new SBI();
ICICI i=new ICICI();
AXIS a=new AXIS();
System.out.println("SBI Rate of Interest: "+s.getRateOfInterest());
System.out.println("ICICI Rate of Interest: "+i.getRateOfInterest());
System.out.println("AXIS Rate of Interest: "+a.getRateOfInterest());
}
}Output:
SBI Rate of Interest: 8
ICICI Rate of Interest: 7
AXIS Rate of Interest: 9
Leave a Reply