Ruby has a built-in modern set of operators. Operators are a symbol which is used to perform different operations. For example, +, -, /, *, etc.
Types of operators:
- Unary operator
- Airthmetic operator
- Bitwise operator
- Logical operator
- Ternary operator
- Assignment operator
- Comparison operator
- Range operator
Unary Operator
Unary operators expect a single operand to run on.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| ! | Boolean NOT |
| ~ | Bitwise complement |
| + | Unary plus |
Example
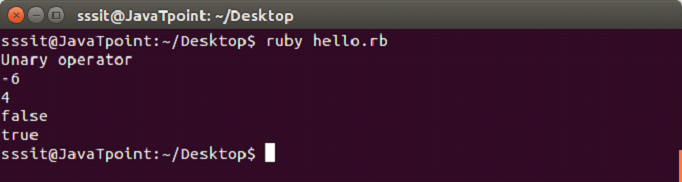
In file hello.rb, write the following code.
#!/usr/bin/ruby -w
puts("Unary operator")
puts(~5)
puts(~-5)
puts(!true)
puts(!false)Output:
Airthmetic Operator
Airthmetic operators take numerical values as operands and return them in a single value.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Adds values from both sides of the operator. |
| – | Subtract values from both sides of the operator. |
| / | Divide left side operand with right side operand. |
| * | Multiply values from both sides of the operator. |
| ** | Right side operand becomes the exponent of left side operand. |
| % | Divide left side operand with right side operand returning remainder. |
Example
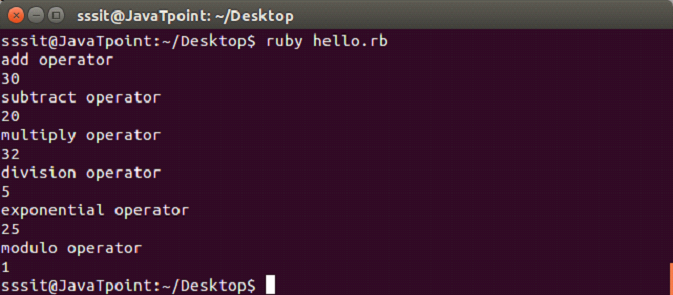
In file hello.rb, write the following code.
#!/usr/bin/ruby -w
puts("add operator")
puts(10 + 20)
puts("subtract operator")
puts(35 - 15)
puts("multiply operator")
puts(4 * 8)
puts("division operator")
puts(25 / 5)
puts("exponential operator")
puts(5 ** 2)
puts("modulo operator")
puts(25 % 4)Output:
Bitwise Operator
Bitwise operators work on bits operands.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| & | AND operator |
| | | OR operator |
| << | Left shift operator |
| >> | Right shift operator |
| ^ | XOR operator |
| ~ | Complement operator |
Logical Operator
Logical operators work on bits operands.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| && | AND operator |
| || | OR operator |
Ternary Operator
Ternary operators first check whether given conditions are true or false, then execute the condition.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| ?: | Conditional expression |
Example
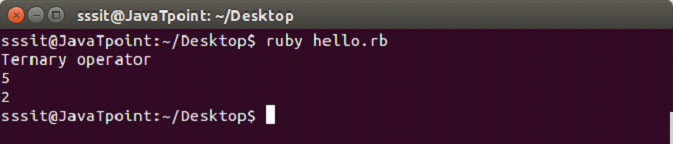
In file hello.rb, write the following code.
#!/usr/bin/ruby -w
puts("Ternary operator")
puts(2<5 ? 5:2)
puts(5<2 ? 5:2)Output:
Assignment Operator
Assignment operator assign a value to the operands.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| = | Simple assignment operator |
| += | Add assignment operator |
| -= | subtract assignment operator |
| *= | Multiply assignment operator |
| /= | Divide assignment operator |
| %= | Modulus assignment operator |
| **= | Exponential assignment operator |
Comparison Operator
Comparison operators compare two operands.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| == | Equal operator |
| != | Not equal operator |
| > | left operand is greater than right operand |
| < | Right operand is greater than left operand |
| >= | Left operand is greater than or equal to right operand |
| <= | Right operand is greater than or equal to left operand |
| <=> | Combined comparison operator |
| .eql? | Checks for equality and type of the operands |
| equal? | Checks for the object ID |
Example
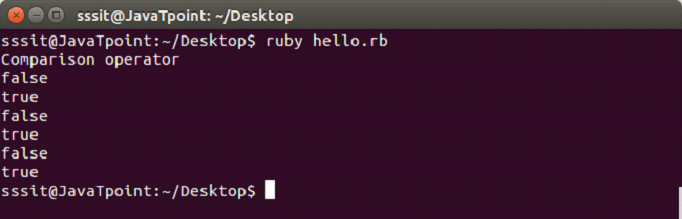
In file hello.rb, write the following code.
#!/usr/bin/ruby -w
puts("Comparison operator")
puts(2 == 5)
puts(2 != 5)
puts(2 > 5)
puts(2 < 5)
puts(2 >= 5)
puts(2 <= 5)Output:
Range Operator
Range operators create a range of successive values consisting of a start, end and range of values in between.
The (..) creates a range including the last term and (…) creates a range excluding the last term.
For example, for the range of 1..5, output will range from 1 to 5.
and for the range of 1…5, output will range from 1 to 4.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| .. | Range is inclusive of the last term |
| … | Range is exclusive of the last term |
Leave a Reply