Data types represents a type of data such as text, string, numbers, etc. There are different data types in Ruby:
- Numbers
- Strings
- Symbols
- Hashes
- Arrays
- Booleans
Numbers
Integers and floating point numbers come in the category of numbers.
Integers are held internally in binary form. Integer numbers are numbers without a fraction. According to their size, there are two types of integers. One is Bignum and other is Fixnum.
| Class | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Fixnum | They are normal numbers | 1 |
| Bignum | They are big numbers | 111111111111 |
| Float | Decimal numbers | 3.0 |
| Complex | Imaginary numbers | 4 + 3i |
| Rational | They are fractional numbers | 9/4 |
| BigDecimal | Precision decimal numbers | 6.0 |
Example:
- In a calculation if integers are used, then only integers will be returned back.
- In a calculation if float type is used, then only float will be returned back.
- In case of dvision, following output will appear.
Strings
A string is a group of letters that represent a sentence or a word. Strings are defined by enclosing a text within single (‘) or double (“) quote.
Example:
- Two strings can be concatenated using + sign in between them.
- Multiplying a number string with a number will repeat the string as many times.
Symbols
Symbols are like strings. A symbol is preceded by a colon (:). For example,
:abcd They do not contain spaces. Symbols containing multiple words are written with (_). One difference between string and symbol is that, if text is a data then it is a string but if it is a code it is a symbol.
Symbols are unique identifiers and represent static values, while string represent values that change.
Example:
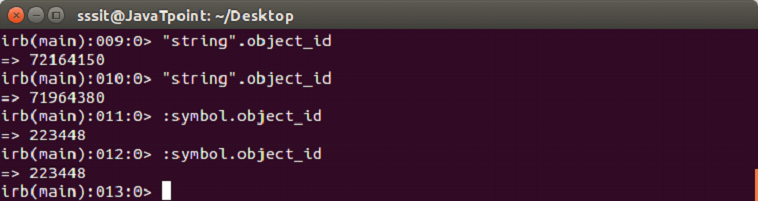
In the above snapshot, two different object_id is created for string but for symbol same object_id is created.
Hashes
A hash assign its values to its keys. They can be looked up by their keys. Value to a key is assigned by => sign. A key/value pair is separated with a comma between them and all the pairs are enclosed within curly braces. For example,
{“Akash” => “Physics”, “Ankit” => “Chemistry”, “Aman” => “Maths”}
Example:
#!/usr/bin/ruby
data = {"Akash" => "Physics", "Ankit" => "Chemistry", "Aman" => "Maths"}
puts data["Akash"]
puts data["Ankit"]
puts data["Aman"]Output:
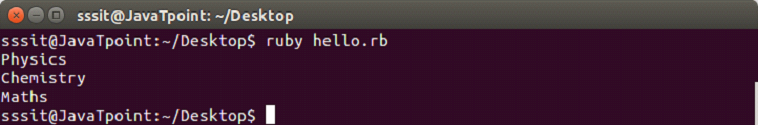
Arrays
An array stroes data or list of data. It can contain all types of data. Data in an array are separated by comma in between them and are enclosed by square bracket. For example,
["Akash", "Ankit", "Aman"] Elements from an array are retrieved by their position. The position of elements in an array starts with 0.
Example:
#!/usr/bin/ruby
data = ["Akash", "Ankit", "Aman"]
puts data[0]
puts data[1]
puts data[2]Output:
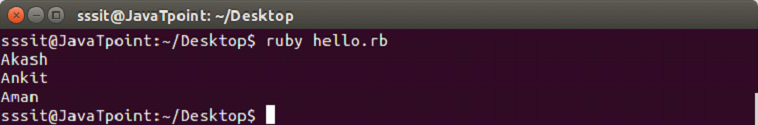
Leave a Reply