An HTML file is made of elements. These elements are responsible for creating web pages and define content in that webpage. An element in HTML usually consist of a start tag <tag name>, close tag </tag name> and content inserted between them. Technically, an element is a collection of start tag, attributes, end tag, content between them.
Note: Some elements does not have end tag and content, these elements are termed as empty elements or self-closing element or void elements.
Such as:
<p> Hello world!!! </p> Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>WebPage</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is my first web page</h1>
<h2> How it looks?</h2>
<p>It looks Nice!!!!!</p>
</body>
</html>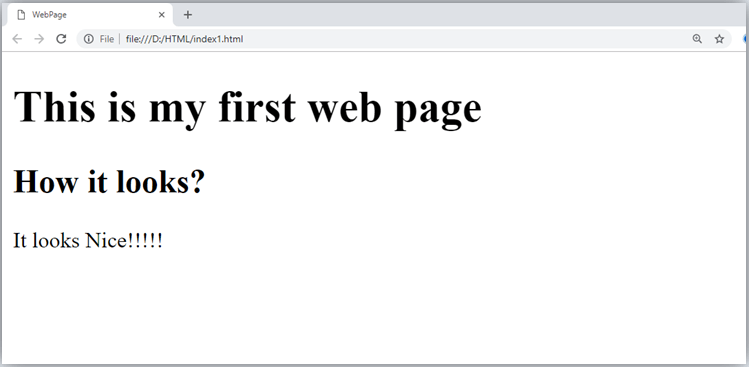
- All the content written between body elements are visible on web page.
Void element: All the elements in HTML do not require to have start tag and end tag, some elements does not have content and end tag such elements are known as Void elements or empty elements. These elements are also called as unpaired tag.
Some Void elements are <br> (represents a line break) , <hr>(represents a horizontal line), etc.
Nested HTML Elements: HTML can be nested, which means an element can contain another element.
Block-level and Inline HTML elements
For the default display and styling purpose in HTML, all the elements are divided into two categories:
- Block-level element
- Inline element
Block-level element:
- These are the elements, which structure main part of web page, by dividing a page into coherent blocks.
- A block-level element always start with new line and takes the full width of web page, from left to right.
- These elements can contain block-level as well as inline elements.
Following are the block-level elements in HTML.
<address>, <article>, <aside>, <blockquote>, <canvas>, <dd>, <div>, <dl>, <dt>, <fieldset>, <figcaption>, <figure>, <footer>, <form>, <h1>-<h6>, <header>, <hr>, <li>, <main>, <nav>, <noscript>, <ol>, <output>, <p>, <pre>, <section>, <table>, <tfoot>, <ul> and <video>.Note: All these elements are described in later chapters.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
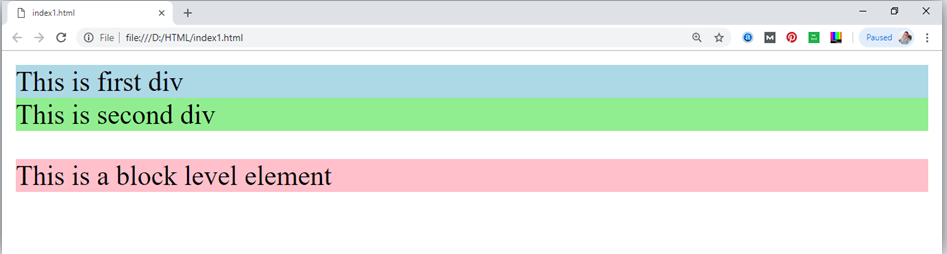
<div style="background-color: lightblue">This is first div</div>
<div style="background-color: lightgreen">This is second div</div>
<p style="background-color: pink">This is a block level element</p>
</body>
</html>Output:
In the above example we have used
tag, which defines a section in a web page, and takes full width of page.
We have used style attribute which is used to styling the HTML content, and the background color are showing that it’s a block level element.
Inline elements:
- Inline elements are those elements, which differentiate the part of a given text and provide it a particular function.
- These elements does not start with new line and take width as per requirement.
- The Inline elements are mostly used with other elements.
<a>, <abbr>, <acronym>, <b>, <bdo>, <big>, <br>, <button>, <cite>, <code>, <dfn>, <em>, <i>, <img>, <input>, <kbd>, <label>, <map>, <object>, <q>, <samp>, <script>, <select>, <small>, <span>, <strong>, <sub>, <sup>, <textarea>, <time>, <tt>, <var>.Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<a href="https://www.javatpoint.com/html-tutorial">Click on link</a>
<span style="background-color: lightblue">this is inline element</span>
<p>This will take width of text only</p>
</body>
</html>Output: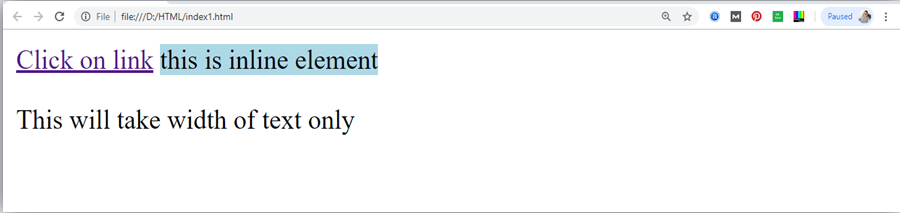
Following is the list of the some main elements used in HTML:
| Start tag | Content | End tag | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| <h1> …… <h6> | These are headings of HTML | </h1>??..</h6> | These elements are used to provide the headings of page. |
| <p> | This is the paragraph | </p> | This element is used to display a content in form of paragraph. |
| <div> | This is div section | </div> | This element is used to provide a section in web page. |
| <br> | This element is used to provide a line break. ( void element) | ||
| <hr> | This element is used to provide a horizontal line. (void element) |
Leave a Reply